Diabetic Eye Disease

Save your sight by controlling diabetes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through diet and exercise can control diabetes and reduce your risk for developing diabetic eye complications. To learn more about how you can help preserve your vision through lifestyle changes, schedule an appointment with Moore’s Retina and Diabetic Eye Specialists.
Moore Eye Institute’s Dr. Leonard Ginsburg, Dr. Shyam Kodati, and Dr. Joshua Steiner are expert diabetic eye specialists who help patients preserve and make the most of their precious vision.
What is Diabetic Eye Disease?
Eye complications stemming from diabetes are common. If left untreated, these conditions lead to deterioration of vision and ultimately, blindness. The two major eye conditions resulting from diabetes are Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) & Macula Edema (DME).

Diabetic Retinopathy
The retina has thousands of small capillaries (retinal blood vessels). The capillaries can be damaged by high blood glucose & blood pressure. There are two main stages:
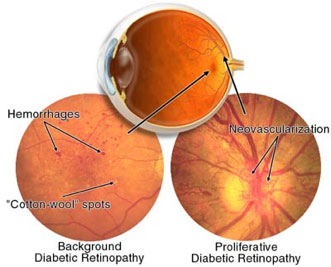
Non-Proliferative
- Early stage, sometimes called background diabetic retinopathy
- Damage has occurred to the retina’s capillaries
- No new capillary growth
- May cause minimal vision loss
Proliferative
- Progressive stage of non-proliferative DR
- Fragile, new capillaries grow on the retina
- Capillaries may bleed or leak
- Complications from the weak capillaries include blurry, darkened vision, and dark spots called floaters
Diabetic Macula Edema
Diabetic macula edema (DME) is a complication from diabetic retinopathy (DR) and the number one cause of permanent vision loss among diabetics. Damaged blood vessels leak fluid into the retina, and the buildup causes swelling and thickening. Only a thorough eye exam can discover this condition.
Diagnosis
Blindness as a result of diabetes is preventable, but an early diagnosis is crucial. Diabetic eye disease can only be detected by a thorough eye exam. Therefore, annual exams are extremely important. Do not wait until vision has deteriorated to have an exam because vision loss may be sudden and not restorable. It is crucial that your blood sugar be consistently controlled for several days before seeing your retina specialist for routine visits.
Treatment Options
- Laser Surgery: Two different laser surgeries are reserved for those with proliferative diabetic retinopathy & diabetic macular edema: pan-retina photocoagulation & focal photocoagulation. The laser treatments seal the leaking capillaries, and slow the swelling that causes vision loss. In most cases, laser treatment only prevents further deterioration, and does not restore lost vision.
- Vitrectomy Surgery: Vitrectomy surgery is generally performed as an outpatient procedure. A surgeon, using an operating microscope and small instruments, removes blood and scar tissue from the eye’s abnormal blood vessel growth. Removing the vitreous hemorrhage allows light to properly focus on the retina and often prevents further bleeding. It is important to follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions carefully so the eye heals properly.
- Medication Injections: Sometimes a steroid medication is used to treat diabetic retinopathy. Alternatively, an anti-VEGF medication can be used to block vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF, a substance that contributes to abnormal blood vessel growth. The medication is injected into the back chamber of the eye after it has been dilated and numbed. The medicine reduces swelling, leakage, and unwanted growth, possibly improving vision.
